Running a business means working with numbers every day—sales, expenses, budgets, inventory, customer data, and employee records. Microsoft Excel is one of the most powerful tools and Excel formula to manage all these tasks quickly and accurately.
Whether you run a shop, manage production, sell online, or operate a service business, learning a few essential Excel formulas can save you hours of work each week.
In this guide from SoluExcel, you’ll learn the 10 most important Excel formulas every business owner should use—each explained with clear Excel tables, cell references, and exact formula locations.
1. SUM() – Add Values Instantly
SUM helps you add sales, expenses, quantities, or totals easily.
Excel Example
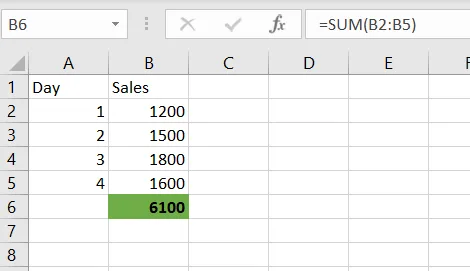
✅ Apply this formula in cell B6
=SUM(B2:B5)This gives the total sales.
2. AVERAGE() – Find the Average
Useful to find average sales, purchase cost, attendance, performance, etc.
Excel Example
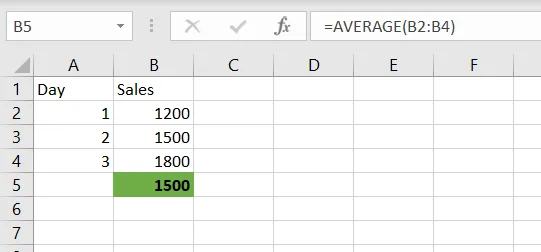
✅ Apply in cell B5
=AVERAGE(B2:B4)3. COUNT() and COUNTA() – Count Rows Quickly
COUNT = counts numbers
COUNTA = counts all non-blank values
Excel Example
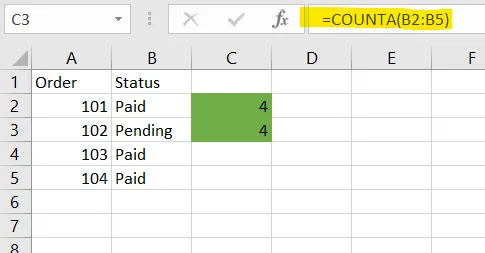
✅ COUNT (Apply in C2):
=COUNT(A2:A5)✅ COUNTA (Apply in C3):
=COUNTA(B2:B5)4. IF() – Make Simple Business Decisions
Use IF() to classify data, set conditions, or auto-judge performance.
Excel Example
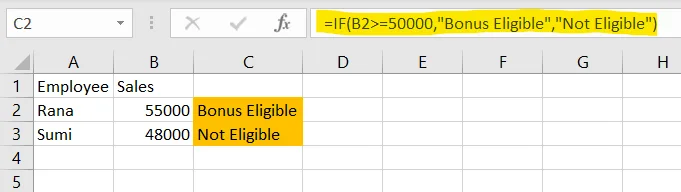
✅ Apply in cell C2
=IF(B2>=50000,"Bonus Eligible","Not Eligible")Copy down to C3 for Sumi.
5. VLOOKUP() – Search Data Instantly
Popular for retrieving prices, product names, customer details, etc.
Excel Example
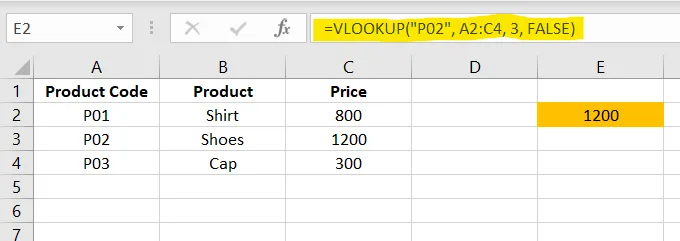
✅ Apply in cell E2
=VLOOKUP("P02", A2:C4, 3, FALSE)6. XLOOKUP() – Modern, Easier Lookup
More powerful than VLOOKUP. Only recommended for all business Excel users.
Excel Example
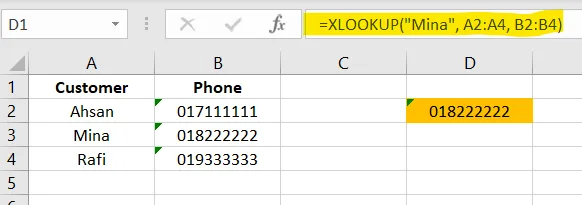
✅ Apply in cell D2
=XLOOKUP("Mina", A2:A4, B2:B4)7. SUMIF() – Add Based on One Condition
Used for product-wise sales, region-wise totals, category totals, etc.
Excel Example
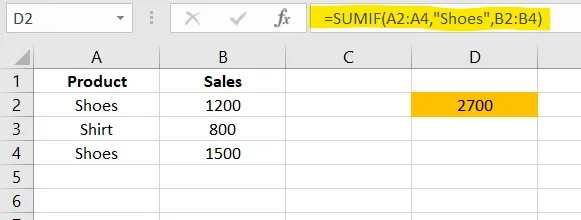
✅ Apply in cell D2
=SUMIF(A2:A4,"Shoes",B2:B4)✅ SUMIFS() – Add Using Multiple Conditions
Excellent for filtered sales or complex reports.
Excel Example
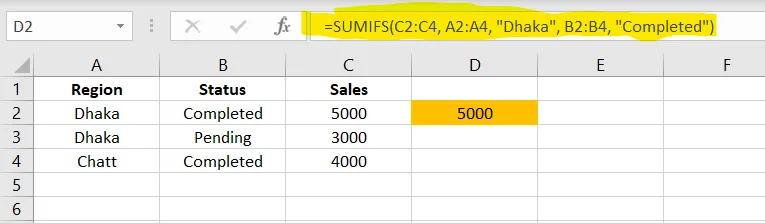
✅ Apply in cell D2
=SUMIFS(C2:C4, A2:A4, "Dhaka", B2:B4, "Completed")8. COUNTIF() – Count Based on a Condition
Great for counting paid invoices, completed tasks, or repeated items.
Excel Example
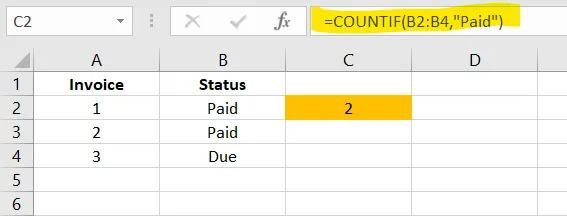
✅ Apply in cell C2
=COUNTIF(B2:B4,"Paid")✅ COUNTIFS() – Count by Multiple Conditions
Excel Example
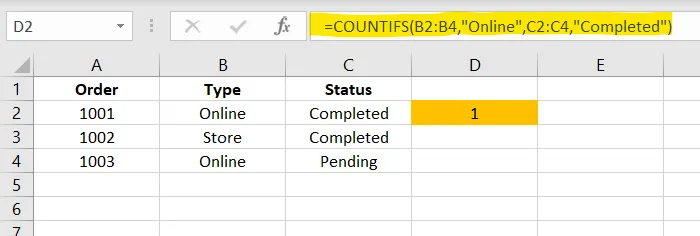
✅ Apply in cell D2
=COUNTIFS(B2:B4,"Online",C2:C4,"Completed")9. CONCATENATE() & TEXTJOIN() – Combine Text Easily
Useful for creating full names, product names, IDs, labels, etc.
Excel Example
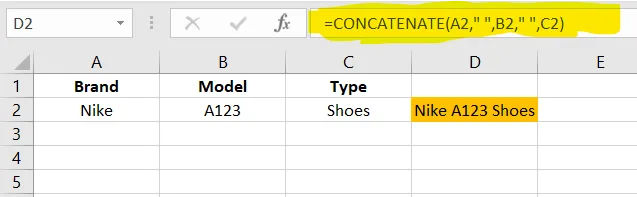
✅ CONCATENATE formula in D2, Business users can use CONCAT()
=CONCAT(A2," ",B2," ",C2)✅ TEXTJOIN formula in D3, this formula is only for Business users
=TEXTJOIN(" - ", TRUE, A2:C2)10. PMT() – Calculate Monthly EMI
Used for business loan planning and installment forecasting.
Excel Input Setup
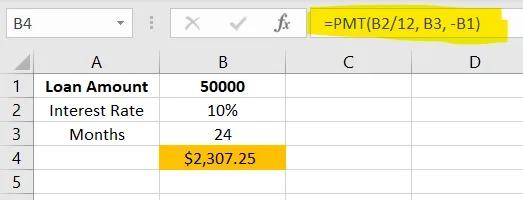
✅ Apply in cell B4
=PMT(B2/12, B3, -B1)Conclusion
These 10 Excel formulas are essential for every business owner because they help:
- Track sales
- Analyze expenses
- Manage customers
- Prepare reports
- Improve productivity
- Make smarter financial decisions
With these examples using actual Excel rows and columns, anyone—even beginners—can apply the formulas immediately.
At SoluExcel, we help business owners and professionals master Excel through blogs, training, dashboards, and custom spreadsheets designed for real business needs. Contact us.